12. Network & Policy » Response¶
Responses are a powerful and flexible way to automate and extend how the system reacts to anomalies detected by Sensors and filtering rules identified by Filters. For each IP, subnet, threshold, or anomaly type, the system can trigger a distinct Response.
To add a new Response, go to Configuration » Network & Policy » [+] and click [Response].
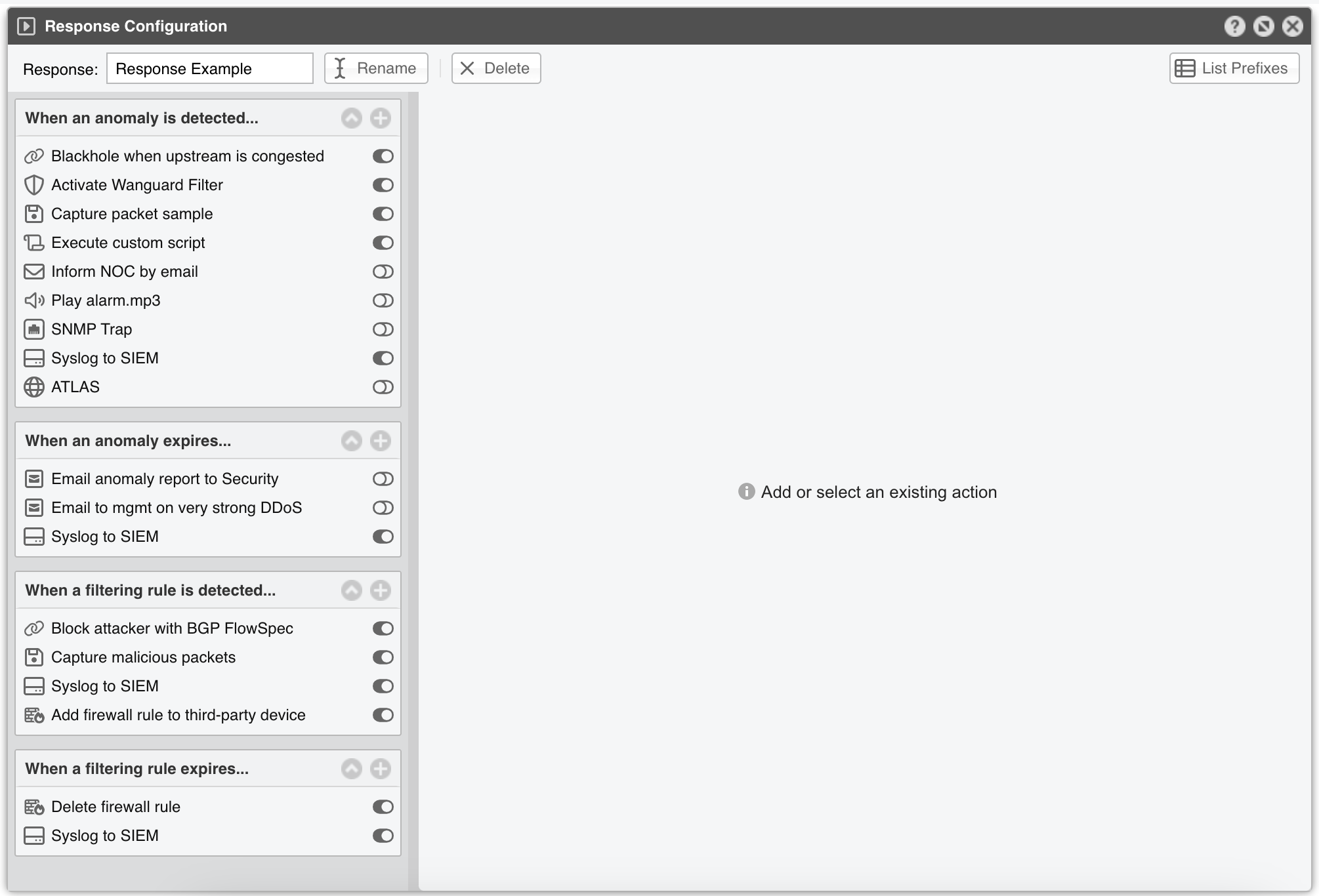
The top bar permits renaming and deleting the Response, as well as showing a list with the IP classes configured to use it.
12.1. Response Actions¶
When invoked by a Sensor or Filter, the Response runs the actions it contains. These built-in modules provide the means to execute commands, send notifications, send BGP routing updates, write logs, etc.
There are two types of actions:
Anomaly Actions are executed by Sensor for each traffic anomaly. To execute such an action immediately upon the detection of an anomaly or while an anomaly is being detected, add it to the When an anomaly is detected… panel. To execute an action when the anomaly expires, add it to the When an anomaly expires… panel
Filtering Rule Actions are executed for each filtering rule identified by Filter. To execute such action immediately upon the identification of a filtering rule or while a filtering rule is being identified, add it to the When a filtering rule is detected.. panel. To execute an action when the filtering rule expires, add it to the When a filtering rule expires… panel
To add an action, click the [+] button from the title bar of the relevant panel from the left-hand side of the window. To view, edit, delete or rename an action, select the action’s name. To enable or disable an action, click the small on/off switch button displayed next to it.
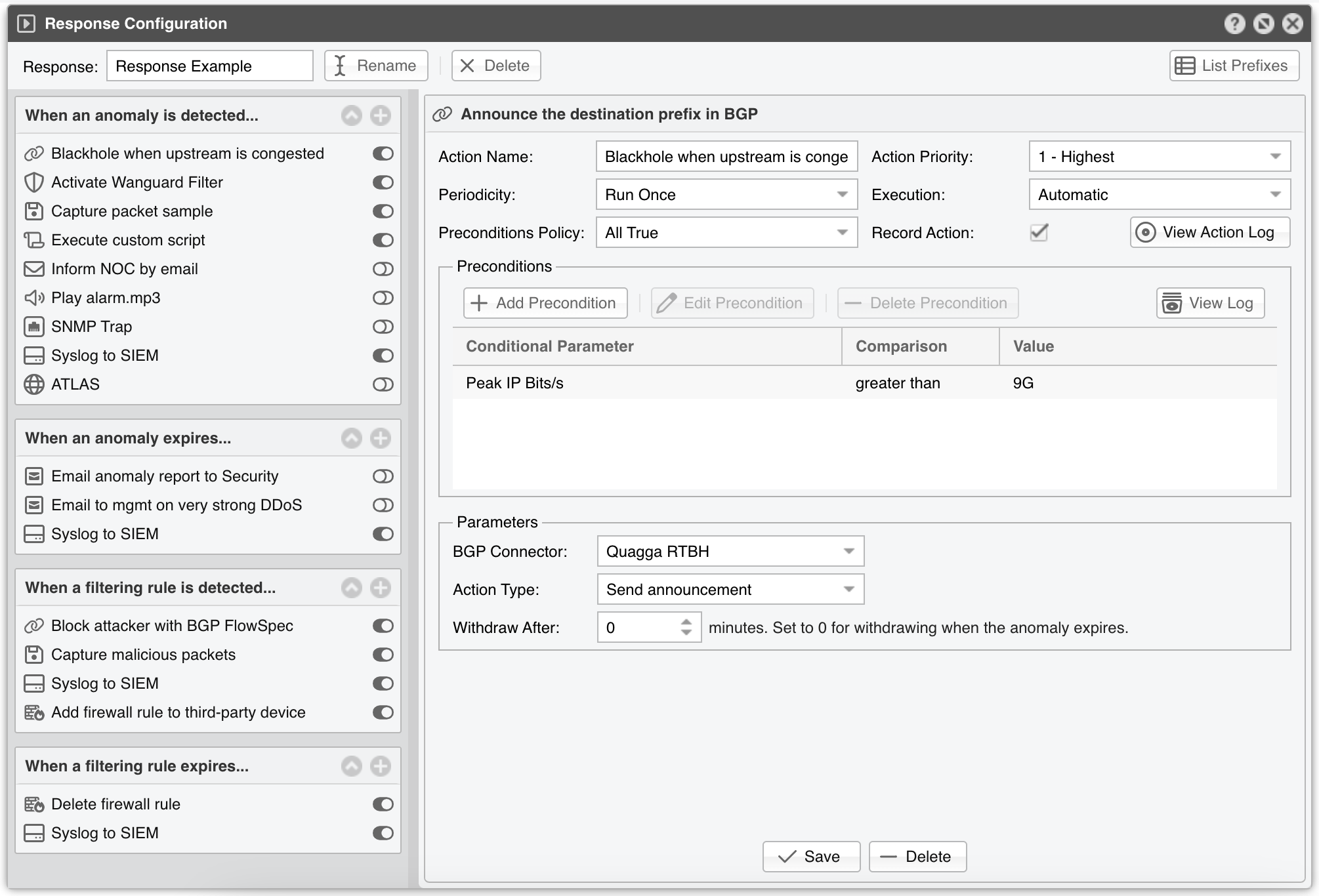
Each action configuration panel contains some action-specific fields. The following fields are present in all actions:
● Action Name – Short description of the action● Priority – Select the order of execution relative to the other actions defined within the same panel. Lower numerical values correspond to increased priority● Periodicity – The action can be executed once per anomaly/filtering rule, or continuously with a frequency of execution of 5 seconds for Packet Sensor, Packet Filter, Sensor Cluster, and Filter Cluster, or 5-60 seconds for Flow Sensor, depending upon its Granularity parameter● Execution – The action can be executed automatically without end-user intervention or manually by an Operator or Administrator that clicks the lightning icon in Reports » Tools » Anomalies● Preconditions Policy – When the first option is selected, the action is executed only when all preconditions (defined below) are evaluated as true. When the second option is selected, the action is executed if at least one precondition is evaluated as true. The action is executed without restrictions when the list of preconditions is empty● Record Action – When checked, the name of the action is recorded and displayed in anomaly reports● Preconditions – May contain rules that, when evaluated as false, will deny the action’s execution. Each precondition is composed of an attribute (conditional parameter), an operator (comparison function), and a user-defined value. The attributes are linked to tokens (internal variables whose values are constantly updated by Sensors and Filters). Appendix 4 - Conditional Parameters & Tokens lists and describes each attribute
Token is a placeholder that can be used as parameter or script argument in most Response actions because, at run-time, the software translates it into the requested value. Each token is defined within curly brackets “{ and }”. Every token is listed in Appendix 4 - Conditional Parameters & Tokens.
12.2. Extending the Built-in Preconditions¶
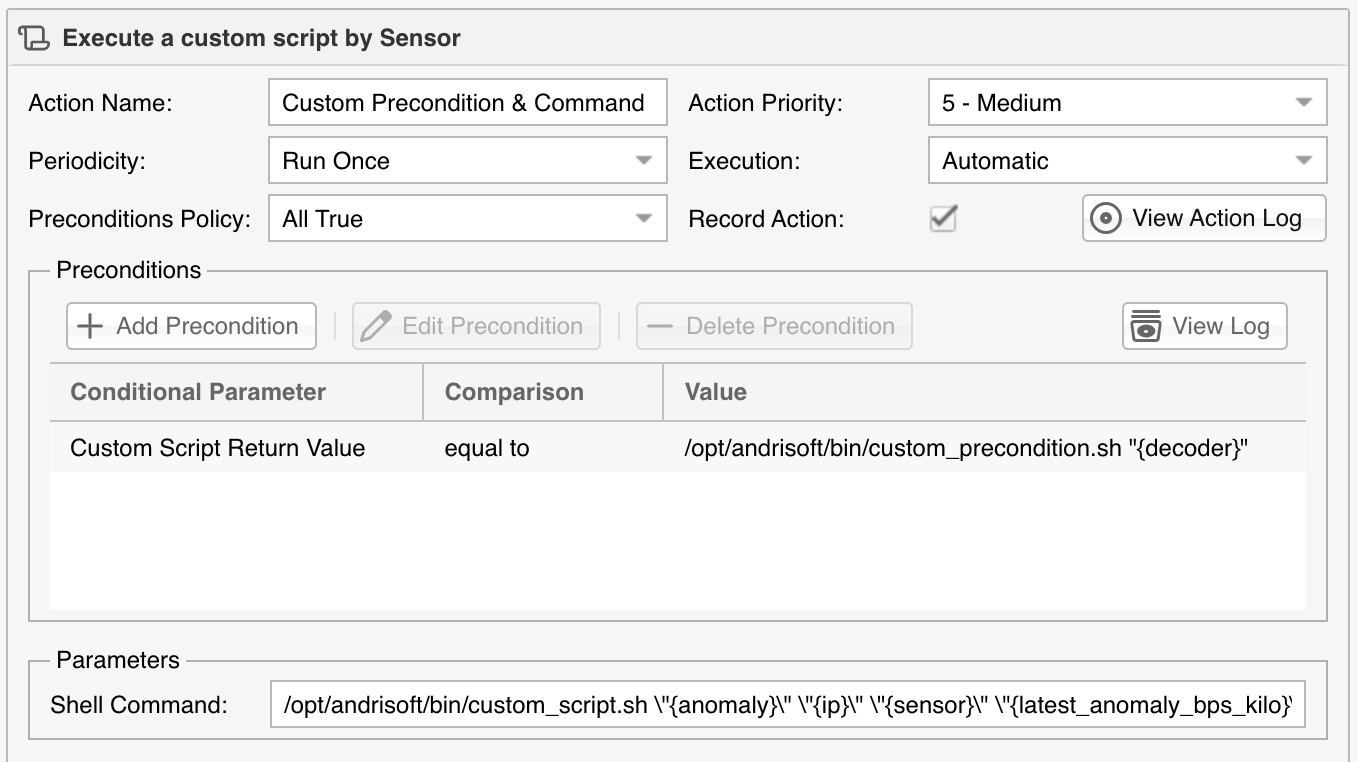
If you need to extend the logic in which actions are allowed to run, use the attribute named Custom Script Return Value. With it, you can implement your own custom precondition, or you can mix logical disjunction and logical conjunction in any way you wish. Just set the Operator field to “equal to”, and in the Value field enter the path to a custom script that accepts tokens (full list on Appendix 4 - Conditional Parameters & Tokens) as arguments.
To access data not related to the current anomaly or filtering rule, or to automate the actions available on Reports » Tools, call the REST API from within your script.
#!/bin/sh
DECODER=$1
if [ "$DECODER" = "NTP" ] || [ "$DECODER" = "SNMP" ];
then
exit 0;
else
exit 1;
fi
12.3. Built-in Response Actions¶
12.3.1. Announce the destination IP address in a BGP routing update¶
Use this action to announce the anomaly’s prefix in a BGP routing update. To prevent uplink network congestion, set up D/RTBH by following Appendix 3 from the User Guide. Add a severity-related Precondition (e.g. Peak Link Severity) to avoid blackholing during weak attacks.
12.3.2. Capture a sample of malicious packets¶
Use this action to capture a packet sample with the anomaly’s traffic. Capturing packets is possible only for anomalies detected by Packet Sensor. Limit the size of the packet dump or use the second Sampling Type option.
12.3.3. Detect filtering rules and mitigate the attack with Wanguard Filter¶
Use this action to activate a Wanguard Filter instance that detects which filtering rules can mitigate the attack. You can define a Precondition to activate the Filter only when the attack is strong enough. Wanguard Filter stops automatically when the anomaly expires.
12.3.4. Execute a command or script¶
Use this action if you want to extend the software’s capabilities with custom scripts or commands. You can pass the tokens listed on Appendix 4 as arguments to the command. Use “sudo” to elevate privileges if the command or script needs root privileges.
12.3.5. Modify an anomaly parameter¶
Use this action to change or update specific details of an anomaly, such as its status, description, or expiration time, based on custom conditions or requirements.
12.3.6. Send a custom email notification¶
Use this action to send informative emails during anomalies. Customize the sender in Configuration » General Settings » Outgoing Email. Emails are delivered by the MTA (Postfix, Qmail, Sendmail) running on the Console server.
12.3.7. Send a custom notification to a third-party provider¶
Use this action to send alerts to an external service provider:
12.3.7.1. Pushover¶
Pushover is a service that allows you to send push notifications to mobile devices and desktops.
12.3.7.2. Slack¶
Slack is an enterprise group chat platform. Wanguard uses the Slack webhooks API to send notifications.
12.3.7.3. Telegram¶
Telegram is a messaging application available for many platforms including iOS, Android, Windows, MacOS and Linux.
12.3.8. Send a custom Syslog message¶
Use this action to send a custom Syslog message. Use Syslog for central log collection, compliance, and reporting to a SIEM. Syslog messages are delivered to the Syslog service running on the Console server.
12.3.9. Send a custom SNMP trap¶
Use this action to send a custom SNMP trap to a management station. SNMP traps are sent using the snmptrap command executed on the Console server.
12.3.10. Send a visual or audio notification to logged-in Console users¶
Use this action to notify all logged-in Console users that an anomaly has been detected. Permit user accounts to receive notifications in Configuration » General Settings » User Management. Upload custom audio notification files in /opt/andrisoft/webroot/mp3.
12.3.11. Participate in A.T.L.A.S. with anomaly statistics¶
Members of A.T.L.A.S. are provided with a globally-scoped view into malicious activities. Enterprise support customers benefit from a Global NOC supervision and managed security services.
12.3.12. Generate an anomaly report and send it by email¶
Use this action to generate a full anomaly report—after the anomaly has finished—and then send it by email to relevant recipients.
12.3.13. Announce a BGP routing update with Flowspec or S/RTBH¶
Use this action to mitigate attacks with Flowspec or S/RTBH. Deploy BGP Flowspec to mitigate attacks by dropping the malicious traffic on the edge router. Filtering rules compatible with Flowspec are listed in Configuration » General Settings » Anomaly Mitigation.
12.3.14. Apply the filtering rule on a third-party inline device¶
Use this action when using a custom script that pushes the filtering rules to an inline third-party device. Install custom ACLs on existing inline appliances such as routers, IPSes, firewalls and load balancers. Helper wrapper scripts not included.
12.3.15. Delete the filtering rule on a third-party inline device¶
Use this action when using a custom script to delete the filtering rules applied on an inline third-party device.
12.3.16. Capture a sample of packets matched by the filtering rule¶
Use this action to capture a packet sample of the traffic that matches the filtering rule. The capturing process stops automatically when the filtering rule expires. Limit the size of the packet dump or use the second Sampling Type option.
12.3.17. Modify a filtering rule parameter¶
Use this action to modify the CIDR mask of the attacker or victim, or to whitelist or stop the filtering rule. For example, you can change the CIDR mask for Flowspec to more efficiently mitigate carpet-bombing attacks. To ensure the CIDR mask changes take effect before the firewall or Flowspec rule is applied, set the priority of this action to Highest.
12.4. Extending the Built-in Actions¶
If you want to extend the number of actions, add the Response action named Execute a command or script. You can pass useful information collected from Wanguard as arguments to your script. Make sure that the script can be run as the “andrisoft” user, and that your script does not require any input from the terminal during execution. You can check if the permissions of the “andrisoft” user are sufficient by executing the script from the CLI with the “sudo -u andrisoft /path/to/your/script.sh” command. It is recommended to output the script’s output to a temporary file, in order to catch any errors, by appending ” > /tmp/script_output.txt 2>&1” to the command. That way you can verify the script’s output in /tmp/script_output.txt.
As an example, the script shown below will write the anomaly number ({anomaly} as 1st argument), attacked IP ({ip} as 2nd argument), detecting Sensor ({sensor} as 3rd argument), and current kbps/s value ({latest_anomaly_bps_kilo} as 4th argument) to a temporary file when the decoder that detected the anomaly is either NTP or SNMP.

#!/bin/sh
echo "Anomaly: $1, IP: $2, Sensor: $3, Kbits/s: $4" > /tmp/test.txt
Note
When writing a script, make sure that it can be accessed and executed by the system account named “andrisoft”. You can check if there are permission-related issues by executing the script manually with “sudo -u andrisoft /path/to/script”. The tokens should be passed within single or double-quotes.