32. Reports » Tools » Firewall¶
The Firewall tab offers detailed information and statistics about the filtering rules (including the associated firewall rules) managed by Wanguard, and provides an easy way for Console users to create their own firewall rules.
A filtering rule in Wanguard Filter describes an attack pattern. Types of filtering rules are found in General Settings » Anomaly Mitigation. Ideally, each filtering rule translates into one or more firewall rules, but this depends on the firewall backend. Netfilter supports all rules; other firewalls may be more limited.
32.1. Active Firewall Rules¶
Displays a list of active firewall rules, either auto-generated by Filters or manually added by Console users.
Administrators and Operators can manually add firewall rules by clicking [Add Firewall Rule], then choosing from the available firewall backends in the dropdown. Firewalls not defined in Filter configurations remain hidden.
32.1.1. Netfilter Firewall¶
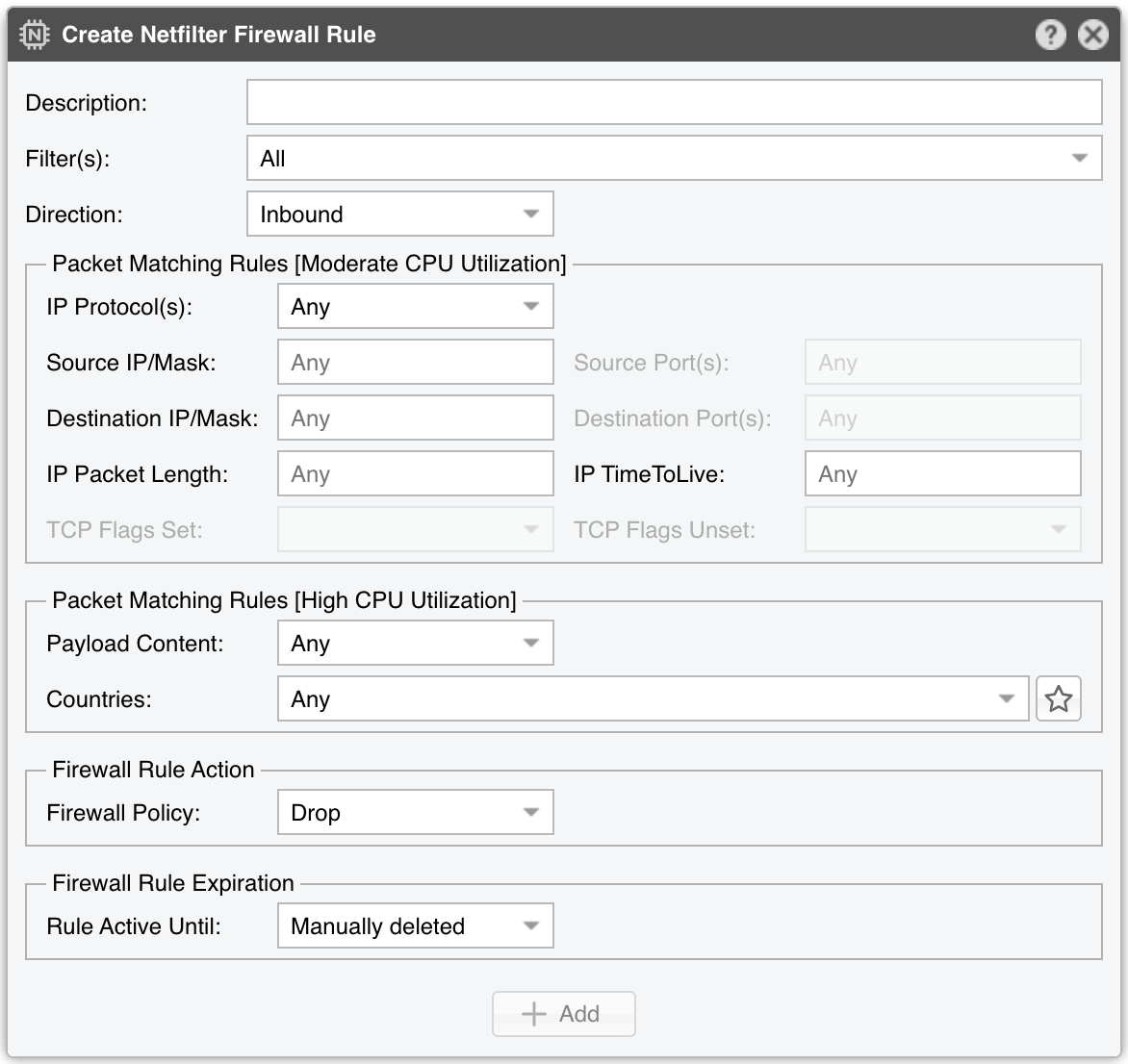
Create Netfilter Firewall Rule window parameters:
● Description – A short name for identifying the firewall rule● Filter(s) – Choose which Filter applies your rule, respecting that Filter’s interface/chain/table settings● Direction – Inbound matches traffic entering the network (where the Filter interface is defined as inbound). Outbound matches outgoing traffic● IP Protocol(s) – One or more IP protocols (e.g., TCP, UDP, SCTP), or Any to match all● Source/Destination IP/mask – Match traffic by source/destination blocks. The CIDR mask is optional; without it, addresses default to /32 (IPv4) or /128 (IPv6)● Source/Destination Port(s) – Specify up to 15 ports or ranges (e.g., “53, 1024:65535”). Field is editable only for TCP, UDP, UDPLITE, DCCP, or SCTP● IP Packet Length – Matches the OSI Layer3 payload length (e.g., Layer4 packet). Use “:” for value ranges● IP TimeToLive – Matches the TTL field in the IP header. Precede the number with “>” or “<” for greater/less than checks● TCP Flags Set/Unset – Select which TCP flags must be set or unset. Flags not specified in either field are ignored● Payload Content – Searches for a string anywhere in the packet. Use cautiously, as it can be CPU-intensive● Country(ies) – Matches traffic by country of origin, requiring the xt_geoip Netfilter module on the server● Firewall Policy – Netfilter firewall action for matched packets:• Drop – Discard the packets• Reject – Discard packets and send an ICMP reply (port unavailable)• Accept – Permit packets to pass• Rate Limit – Allow a limited number of packets or bytes● Rate Limit – The allowed rate of packets per time unit. If suffixed with “b”, rate-limiting uses bytes instead of packets● Rate Limit Hashing – Decide whether to apply rate-limiting globally or per object (e.g., Src. IP, Dst. Port, etc.). For a connection-oriented approach, select all objects. To limit the rate per source IP, choose Src. IP● Rule Active Until – Manually deleted keeps the rule indefinitely. Other options remove the rule once a predefined condition is met
32.1.2. Hardware Offload¶
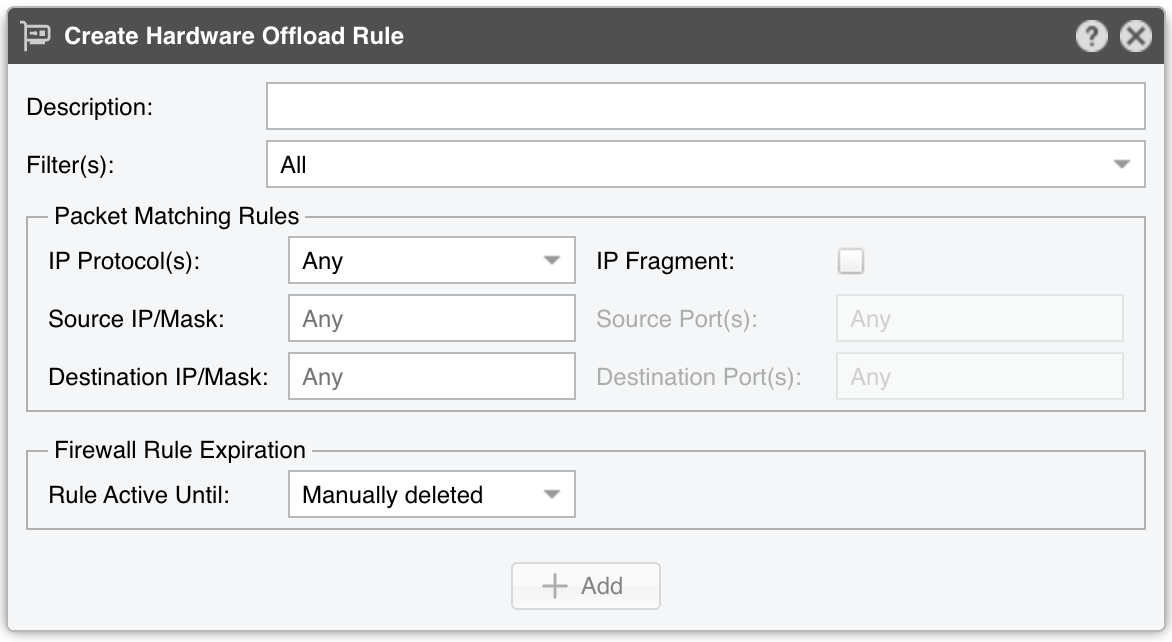
Create Hardware Offloading Rule window parameters:
● Description – A short name identifying the firewall rule● Filter(s) – Choose which Filter applies your rule● IP Protocol(s) – Select one or more protocols (TCP, UDP, etc.) or Any to match all packets● IP Fragment – Matches only fragmented packets● Source/Destination IP/mask – Match traffic by source/destination blocks. The CIDR mask is optional; without it, addresses default to /32 (IPv4) or /128 (IPv6)● Source/Destination Port(s) – Only for TCP, UDP, UDPLITE, DCCP, SCTP. Matches a set of source or destination ports● Rule Active Until – Manually deleted keeps the rule indefinitely. Other options remove the rule once a predefined condition is met
The matched counters are not available in call cases. Chelsio offers partial counters, while Mellanox does not offer any counter information.
32.1.3. Dataplane Firewall¶
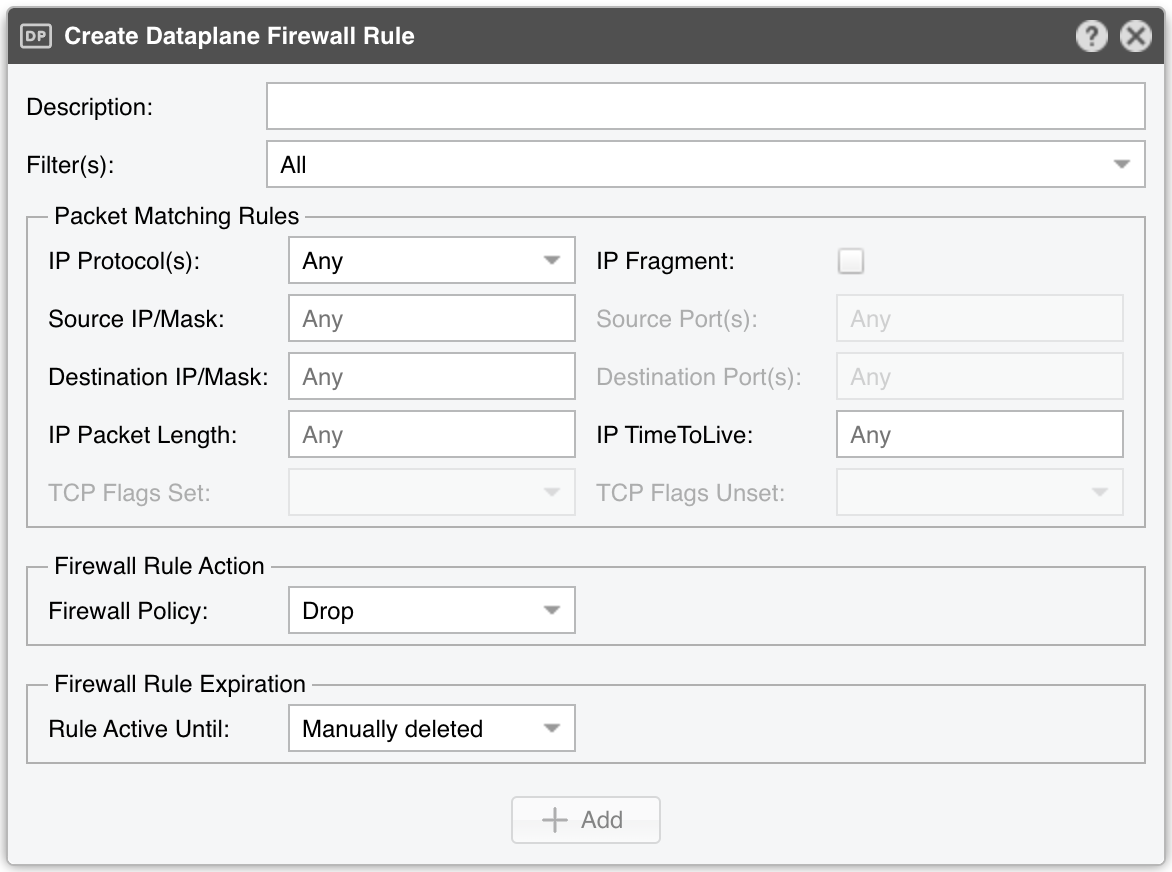
The Create Dataplane Firewall Rule window parameters:
● Description – A short name identifying the firewall rule● Filter(s) – Choose which Filter applies your rule● IP Protocol(s) – Select one or more protocols (TCP, UDP, etc.) or Any to match all packets● IP Fragment – Matches only fragmented packets● Source/Destination IP/mask – Match traffic by source/destination blocks. The CIDR mask is optional; without it, addresses default to /32 (IPv4) or /128 (IPv6)● Source/Destination Port(s) – Only for TCP, UDP, UDPLITE, DCCP, SCTP. Matches a set of source or destination ports● IP Packet Length – Matches the OSI Layer3 payload length (e.g., Layer4 packet)● IP TimeToLive – Matches the TTL field in the IP header● TCP Flags Set/Unset – Select which TCP flags must be set or unset. Flags not specified in either field are ignored● Firewall Policy – Dataplane firewall action for matched packets:• Drop – Discard the packets• Accept – Permit packets to pass• Count – Only count the packets● Rule Active Until – Manually deleted keeps the rule indefinitely. Other options remove the rule once a predefined condition is met
32.2. Filtering Rule Archive¶
Displays all filtering rules detected by the selected Filter(s) over the specified time interval. Several columns are explained in Reports » Tools » Anomalies.
32.3. Filtering Rule Distribution¶
Generates pie charts showing statistics on filtering rules.